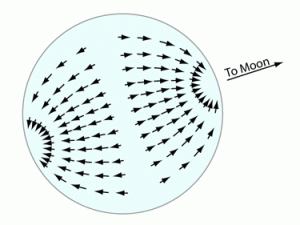
- The gravitational force of the moon may be only 1 ten millionth that of the Earth but when you combine it with other forces, like that of Earth’s centrifugal force (the force created by the Earth’s spinning), tides appear.

- The sun also has a gravitational force which acts upon the oceans, but this is only 46% of the strength of the Moon’s.
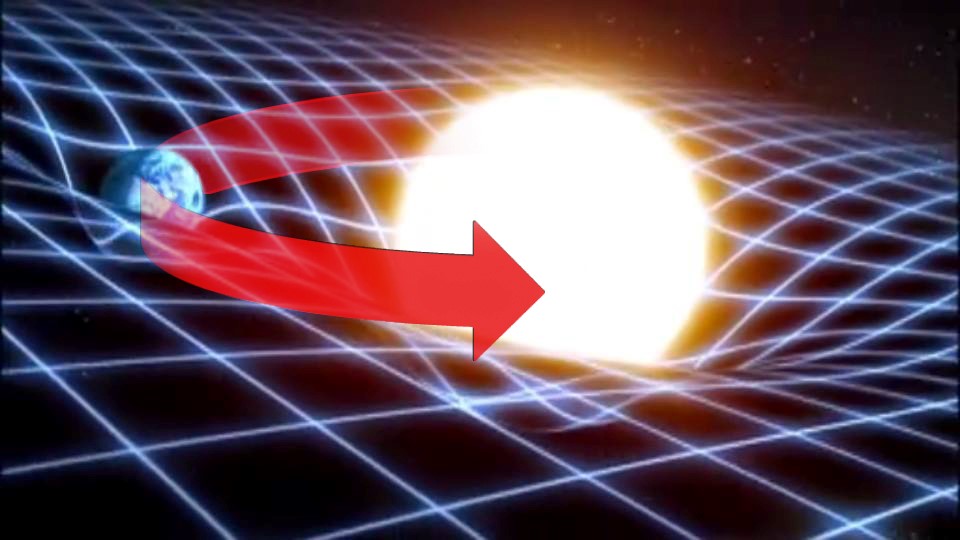
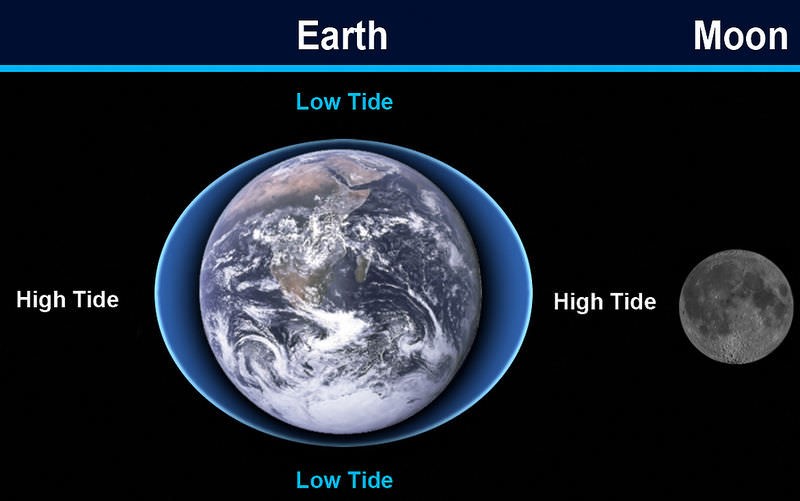
- Contrary to popular belief tides are not the direct result of the moon pulling on the oceans. Tides occur because of the opposition of forces between the Earth’s Gravity and the Moon’s.
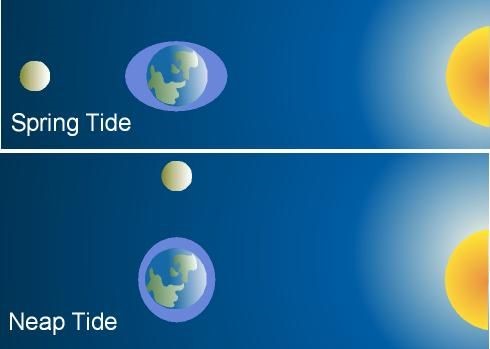
- When the Moon and the Sun are on the same side of the earth (at a New moon) or on opposite sides (at a full moon), we get what is called a ‘Spring Tide’.

- When the moon is in either the first of last quarter of its phases, when the moon is at a right angle to the Sun and the Earth, we get tidal bulges which are known as ‘Neap Tides’.

- Spring and Neap tides are about 20% higher or lower than normal.
- Far out at sea, the difference in tides is usually less than half a metre.

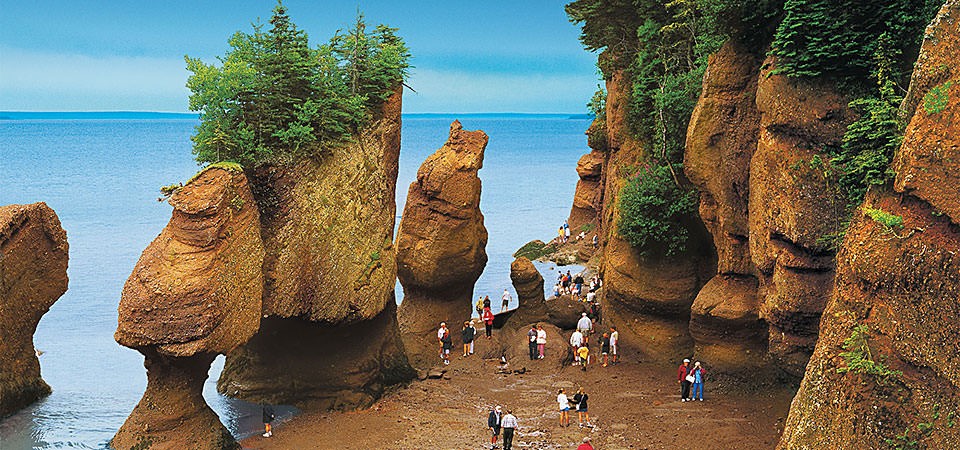
- The biggest tide in the world happens a few times a year in the Bay of Fundy which separates Nova Scotia and New Brunswick in Canada. The tidal difference can be as high as 16.3 metres, the same height as a three-storey building!

- Because the moon moves around the earth and a different speed than the Earth spins on its axis the moon is not always in the same place every day meaning that the times of high and low tides changes by 50 minutes every day. Which is why it is a good idea to check the tides before you go to the beach.

- The type of gravitational force that causes tides is called “Tractive” force.